Last fall, we discussed five important aspects of culture, specifically those that are often invisible. It’s easy to see how people from various cultural backgrounds may behave differently, but it’s more difficult to understand their assumptions, values, and beliefs that drive those behaviors. Not understanding some of the reasons for behaviors can make cross-cultural interactions awkward, anxiety-producing, or downright hostile.
English learners in your class likely come from cultural backgrounds that differ from your own. As a busy teacher, it can be easy to overlook the ways these cultural differences show themselves. You may write off an “odd” behavior as just that—unusual. You might consider their behaviors as indicative of emotional, behavioral, or learning needs that require special testing and instruction. None of these assumptions may be correct if the student is simply behaving according to their cultural norms.
A good way to begin to understand your students’ cultural norms is to read the Look Beneath the Surface series of articles from last fall.
An additional step for learning about specific national cultures is to use the Hofstede Insights Country Comparison Tool.
Using the tool is easy. Just choose countries from the list that you wish to compare. Like this….
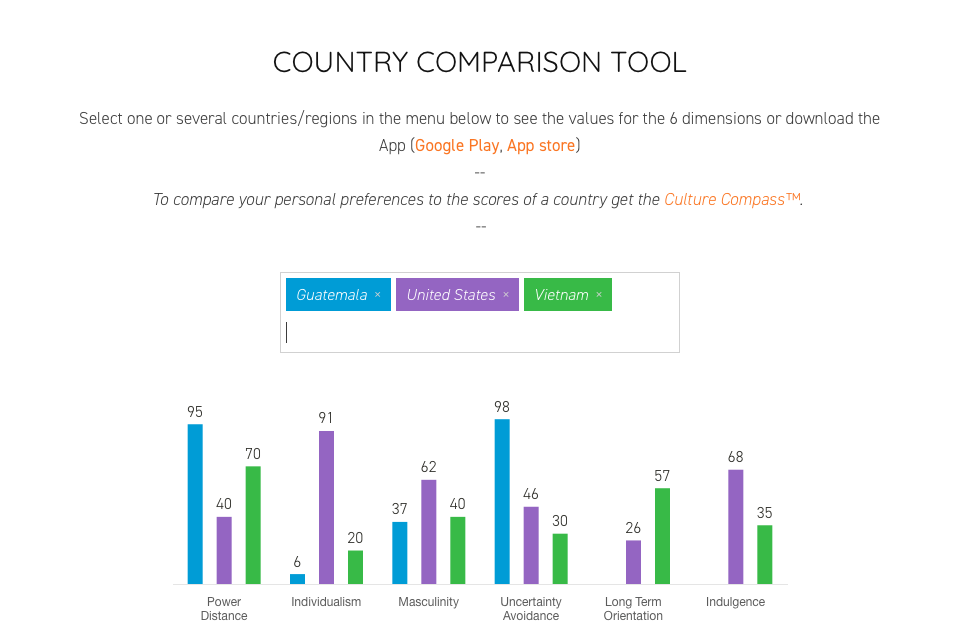
In the following example, I chose to compare the United States, Guatemala, and Vietnam. The tool shows scores for several invisible dimensions of cultures from each country. At a glance, you can see that both Guatemala and Vietnam have much higher power distance than the United States, but they are much lower on the Individualism scale, meaning they are Collectivist cultures. The scores range from 0 to 100.
Sometimes it is helpful to read more detailed information about the scoring. As this picture below shows, you can look deeper into the tool to read about what high power distance likely means in Guatemalan culture. Reading this information will provide insights into how this aspect drives stereotypical Guatemalan behavior, which can be compared to the assumptions, values, and beliefs of other cultural groups. Understanding the foundations on which behavior is built provides insights into where and why cultural miscommunication may occur.

Conveniently, this information can also be accessed through the Hofstede Insights mobile app found in the App Store or in Google Play.
Download the app today or check out the link to the tool provided above. You just never know what you might learn about your students and how it could affect your instruction for the better!